What you should know
Risks for transmission
- Gonorrhea is a bacterial infection that is spread through unprotected oral, vaginal or anal sex with an infected partner, including through mutual masturbation and sharing of sex toys.
- Penetration and ejaculation are not required for transmission.
- It can be passed from an infected mother to her infant during birth.
Symptoms
- Most women do not develop any symptoms of gonorrhea, but most men do.
- When symptoms do occur, they might only appear 2-7 days after infection.
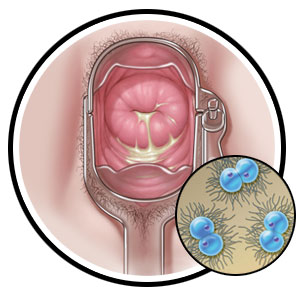
Female:
- Increased vaginal discharge
- Pain in the abdomen or in the lower back
- Vaginal bleeding after intercourse or between menstrual periods
- Pain during intercourse
Both female and male:
- Painful urination
- Pain, itching, bleeding, and/or mucus discharge of the rectum
- Redness, itching, and/or discharges of the eyes (for gonorrhea in the eyes)
- Throat infection
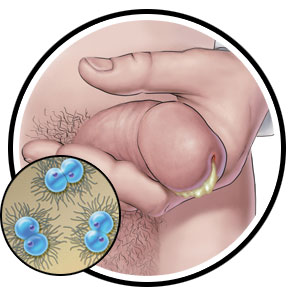
Male:
- Thick, yellowish-green discharge from penis
- Testicular pain or swelling
- Itching penis
Prevention
- Condoms can help prevent the spread of gonorrhea during anal or vaginal sex, and condoms or dental dams can be used for protection during oral sex.
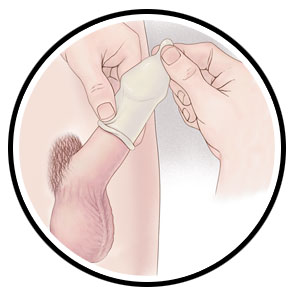
Testing
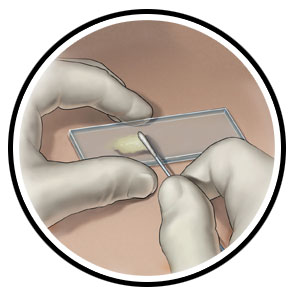
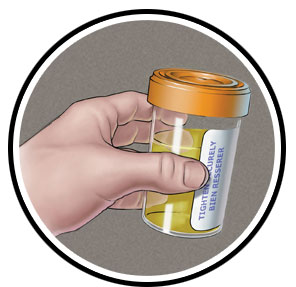
- Testing for gonorrhea is done by swabbing the infected area or by using a urine sample.
Treatment
- Gonorrhea is treated usually with dual therapy antibiotics, as a single dose by mouth and a single muscular injection.
- Sexual partners who have had contact with an infected person within 60 days of diagnosis require testing and treatment.
- Anyone treated for gonorrhea should be re-tested 6 months afterwards.
- Patients treated for gonorrhea should also be treated for chlamydia.
- Don’t have sex until treatment is complete (7 days after a single dose treatment).
Complications
If left untreated, gonorrhea can cause serious health complications.
- In women, gonorrhea can spread from the cervix to the uterus and fallopian tubes, an infection called Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID). This can then lead to chronic pelvic pain, risk of ectopic pregnancies, and infertility.
- In men, gonorrhea can cause testes infection.
- For pregnant women, gonorrhea can also cause miscarriage, preterm birth, premature rupture of membranes, or infection. It can be passed from mother to child during birth, causing an eye infection or a severe infection in the blood.
- In both men and women, gonorrhea can cause arthritis, infertility, or severe infection in the blood.